Gone are the days when finding a job involved walking into a business with a WordPerfect resume in hand. Prior to social media networking, cloud, mobile applications, and big data, there was almost no publicly available data or information about your workforce or your competition. You had to rely on sheer instinct and “gut feel” when it came to hiring and retaining employees, because there was no other way to empirically measure and analyze data to make more informed decisions.
Even today, some are still being caught by surprise when a star performer announces in a Friday afternoon meeting that he or she is leaving.
What if those conversations could be changed? Today’s leading companies are using people analytics to compete and win the war on talent. They quickly understood that the changes that shook the marketing world in the late 1990s (which were driven by the emergence of the World Wide Web and its influx of data), can be applied to HR/talent acquisition. As a result, they have started using similar analytics techniques to optimize every stage of their talent life cycle management.
The vast amounts of data available have changed both how seekers find their jobs and how companies attract and retain their talent. The rise of big data and analytics is changing the way the world does business, and this applies to talent management as well. When you combine the way technology has changed the speed at which people communicate with the vast insights available on human behavior, you get knowledge that can be applied to the workforce. This can help us predict employee behavior, identify valuable talent like never before, match capabilities to market needs, retain the best people, and act on proven insights to drive better business outcomes.
Sounds great, right? While all this information is readily available, companies often are overwhelmed by the data at their disposal, and fail to analyze it against critical workforce questions. The issue today is not the lack of data, but rather how to prioritize, access, and use the deluge of talent data in real time so that it has its greatest impact on the business.
When you consider that studies have shown that the total human capital cost accounts for 60 to 70 percent of all companies’ expenses, it becomes clear that organizations need to take the guesswork out of their talent management cycle by using analytics, and analytics insights to optimize outcomes.
What is People Analytics, Anyway?
As the complexity of workforce challenges continues to rise, so too does the demand for more quantitative approaches to address the increasingly difficult people-related questions central to organizational success. Formerly called talent analytics or workforce analytics, people analytics are a set of analytics that starts with a talent-management business question (for instance, who should you attract, acquire, develop, promote, or retain), and integrates internal and external talent data (this refers to publicly available data, company data, and labor market data) to make a prediction about workforce behaviors and actions across the organization, and enables you to track the results.
The power of people analytics is in its ability to challenge conventional wisdom, influence behavior, enable talent and business leaders to make and execute smarter and more strategic workforce decisions, and ultimately impact business outcomes.
Solving for Today’s Complex Challenges
Based on my first-hand experience building and implementing advanced business analytics teams and solutions, and enriched by my conversations with people across the world about their most pressing challenges while presenting at conferences, panel discussions, and keynotes over the past 10 years, I realized that there was an opportunity to apply traditional business analytics techniques to workforce and human capital challenges. I then spoke with and conducted research with more than 340 industry leaders and experts across the human-resources discipline, from talent acquisition and retention, talent development to staffing, data analysts, and business partners, to learn about their most important business priorities and challenges.
Four major challenges and seven talent management priorities emerged from my research and interviews with them:
- Challenge 1: Silos and disconnected data and tools: Nearly every individual I’ve spoken with has wrestled, or is wrestling, with massive amounts of internal and external siloed data, and different tools that don’t integrate with one another.
- Challenge 2: Lack of optimization: Although the data exists, there is a pressing need to cull the right information in order to optimize the stages of the talent management life cycle.
- Challenge 3: Analytics expertise: Beyond reporting, most businesses do not have the qualified resources needed to create and translate the data story into business outcomes.
- Challenge 4: Predictive insights: There is a lack of insight, despite the deluge of data, when it comes to determining trends that can anticipate future workforce behavior and organizational needs.
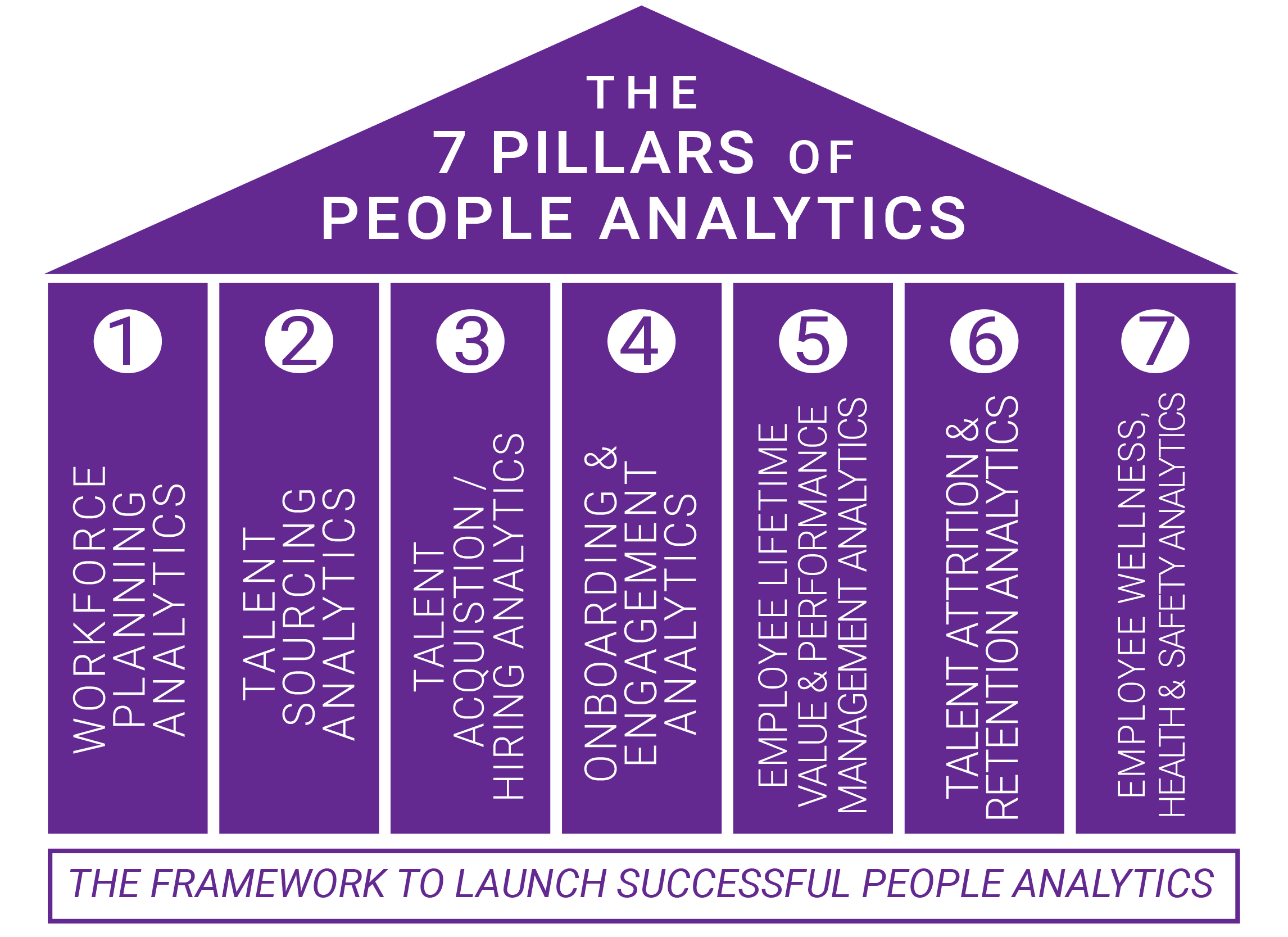
My colleagues and thought leaders throughout the industry also shared with me the stages of their talent life cycle management that they continually seek to optimize in order to drive better business performance. The result is the Seven Pillars of People Analytics:
- Workforce planning
- Talent Sourcing
- Talent Acquisition
- Onboarding Culture Fit and Engagement
- Performance Management and Employee Lifetime Value
- Talent Retention
- Employee Wellness and Well-being
Using the 7 Pillars to Build a Stronger Organization
The seven pillars of people analytics success are obtained by applying the Analytics IMPACT Cycle to the seven most critical talent management stages defined above. This requires the identification of the seven stages of talent management cycle and the application of the Analytics IMPACT Cycle, which is made up of the following steps:
- Identify the question: In a nonintrusive way, help your business partner identify the critical business question(s) he or she needs help in answering.
- Master the data: This is the analyst’s sweet spot — assembling, analyzing, and synthesizing all available information that will help in answering the critical business question
- Provide the meaning: Articulate clear and concise interpretations of the data and visuals in the context of the critical business questions that were identified.
- Actionable recommendations: Provide thoughtful business recommendations based on your interpretation of the data.
- Communicate insights: Focus on a multi-pronged communication strategy that will get your insights as far and as wide into the organization as possible.
- Track outcomes: Set up a way to track the impact of your insights.

Applying the Analytics IMPACT Cycle to the seven stages of talent life cycle management to create business value from its data (regardless of whether it is big or little) is what I called the Seven Pillars of People Analytics Success, or the framework of people analytics success.
Putting People Analytics to Work
The People Analytics Success Pillar framework is designed to help business leaders extract value from multiple talent data streams across the organization. The following insights are grounded in lessons I learned first-hand from my experiences in analytics leadership positions, where it was my job to help companies make the most of their data assets.
Regardless of the specific situation, the pillar framework can be thought of as similar to the foundation of a house: One needs all of the areas of support in order to make the house stand strong and not collapse. Therefore, the goal of the PASP framework is to focus the organization’s attention on the areas that are key to people analytics success and that will lead to the greatest return on investment. This framework is how HR/TA teams can build business cases and address key C-suite challenges, offering practical guidance for chief operating officers, chief financial officers, chief health officers (CHOs), chief people officers, chief human resources officers, chief marketing officers, chief talent officers, and heads of staffing.
The PASP captures the key activities and similarities that thriving and successful companies implement in order to stay competitive. It contains seven pillars that are critical to successful people analytics implementation:
- Workforce Planning Analytics
- Talent Sourcing Analytics
- Talent Acquisition Analytics
- Onboarding Engagement and Culture Fit
- Performance Management Analytics and Employee Lifetime Value
- Talent Retention Analytics
- Employee Wellness Health and Safety
This framework should be used as a starting point for your organization, used as a blueprint to take your talent management to the next level. Here is how the pillars work:
Workforce Planning Pillar
Workforce planning refers to the process that helps identify what talent your organization will require to achieve its business goals and business objectives — from current needs to future needs and succession planning.
The Workforce Planning Pillar is about using the questions from the Analytics IMPACT Cycle to proactively plan for the right number of employees, who have the right skill sets, at the right place, at the right time, and at the optimal cost, so that your organization can drive performance. It also helps to anticipate workforce needs by economic cycles.
Talent Sourcing Pillar
Talent sourcing analytics is about using the IMPACT Cycle to harness all the data and talent information available to optimize your sourcing results. Successfully searching for candidates in today’s globally competitive talent market requires an approach that allows you to accurately identify and locate candidates, assess their potential, and engage with them in an easy way. The sourcing analytics pillar is about using data to optimize your sourcing results, including how to determine staffing resources, and what channels and sources of hire will be most effective in engaging potential candidates.
Talent Acquisition Pillar
Whether you have a small company or manage a large organization with thousands of employees, choosing the wrong candidates can have a lethal impact on your business. So ensuring that your organization makes wise talent investments is critical to both long-term and short-term success.
The acquisition analytics pillar uses the Analytics IMPACT Cycle to preselect who to meet for an interview, how to optimize the interview process, help to determine the best ways to vet candidates and set up interview questions, and assist with creating some tests that can be used to analyze the correlation between a candidate’s performance during the interview and his or her performance in a particular job function.
Onboarding and Culture Fit Pillar
Onboarding
Once the right candidates have been hired, they need to be properly onboarded to ensure they are aligned with primary business goals and the overall mission of the company. New hires need to have the best first impression of you as an HR professional, as well as their manager, and of your company.
Talent onboarding is as an ongoing talent management process that consists of introducing, training, mentoring, coaching, and integrating a new hire to the core values, business vision, and overall culture of an organization in order to secure new employee loyalty and productivity. Analytics from the onboarding and engagement analytics pillar can be used to enhance a new hire’s first impression and create business value from your onboarding activities and efforts. It will also help your organization address vital talent management questions, including:
- How can a business improve time to performance?
- Does your new employee fit with company culture?
- What is an appropriate talent onboarding budget?
- What impact does talent onboarding have on employee turnover?
- What is the impact of talent onboarding on employee loyalty?
Culture fit
In this diverse workforce demographic where multiple generations have to work together, cultural fit is critical for the successful integration of your new hire, and employee and company value mismatches are one of the major reasons for early turnover. Employee lifetime value is secured through a continuous process of engagement, assessment, and promotion.
Engagement
To stay competitive, keep your employees fully engaged in order to meet and exceed your customers’ expectations and achieve your corporate goals. A key component to accomplishing this is monitoring the engagement level of your employee population.
I define an engaged employee as happy, enthusiastic, motivated, and an individual who eagerly relishes the challenges of her job. Analytics helps to understand the various drivers of employee engagement that deliver happier, more productive workers, and decrease unplanned turnover.
Applying the IMPACT Cycle can also provide insights on methods for increasing employee engagement via existing channels such as performance appraisals, the voice of the candidate, industry standards, and other metrics that can boost employee satisfaction and assist in paving career pathways.
This pillar can also help organizations assess the correlation between engagement scores and employee performance in the past, present, and future — which is important information for reducing and mitigating the cost of bad hires and ultimately optimizing employees’ lifetime value.
Performance Management, Employee Lifetime Value, & Cost Modeling
Performance management analytics:
Performance management analytics helps employers to regularly assess the performance of their employees and provide frequent feedback and goals to achieve success leveraging analytics and Big Data. It can also help organizations assess how many employees they will need at each level in the coming years, which is how leading companies predict employee promotion and career pathways.
Lifetime value:
The lifetime value of a customer is often defined as “a prediction of the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer,” and most traditional businesses are able to measure the consumer behavior from every angle. We can quote the lifetime value of our customers to three decimal points, though we don’t really know them. Our employee relationships are deeper, longer-term, stickier, and more laden with potential value than customers in almost every industry. Similar advanced analytics can also be applied to the workforce to calculate the lifetime value of an employee in a certain role. With the employee lifetime value data in hand, employers can optimize their proactive and ad-hoc employee retention strategies, and prioritize based upon the value of each member of their workforce segmenting them into categories, such as margin value creator, and proactively determining what it would cost to lose a top performer.
Employee Retention Pillar
This pillar addresses employee churn by analyzing internal and external talent data intelligence, and help an organization address major attrition questions, including:
- Who are the top performers that are at high risk of leaving, and why?
- When are they more likely to quit?
- What proactive actions could be done to retain employees?
Employee retention is about proactively identifying and understanding which of your valuable employees are employees at risk of leaving, and when and why they would leave. Analytics can help to marry employee data, company data, and market data to predict and interpret top-performing employees’ behaviors, giving you competitive insights for your retention strategies.
Employee Wellness, Health, and Safety Pillar
To be successful, organizations have to create and design an environment and culture that promotes the well-being, health, and safety, of their employees. This means finances and resources need to be allocated to support these endeavors, which requires a demonstrable linking of investments in employee health, safety, and well-being to company business performance. Best practices include proactive activities such as wellness visits, preventive checkups, and vaccinations to avoid the high cost of urgent reactive procedures.
Used properly, this pillar provides a competitive advantage that can assist organizations in differentiating themselves from their competition, and further showcase the impact of that investment on their bottom lines by addressing questions such as:
- What is the impact of employee well-being and health on company productivity?
- What is the impact of employee satisfaction on customer satisfaction?
- What is the impact of employee health and well-being on company retention and acquisition metrics?
By investing in programs that promote the health, well-being, and safety of their workforce, companies can increase the happiness of their employees, boosting engagement, and improving the quality of services they provide to the customers with whom they engage on a daily basis — resulting in a healthier company bottom line.
Putting the Power in Your Hands
Armed with the people analytics framework, staffing leaders and business partners can definitively link their actions and activities to positive business outcomes by combining the art of the industry (their experience, expertise, intuition, and storytelling), with science (data intelligence) to address major workforce and business questions to compete and win in a competitive talent marketplace.
To learn more about The power People Analytics, please check out my recently published book: People Analytics in the Era of Big Data : Changing the Way You Attract, Acquire, Develop, and Retain Talent — All graphics presented here were from People Analytics in the Era of Big Data and were with authorization